Common Injection Molding Defects
Most defects in injection molding are related to either the flow of the melted material or its non-uniform cooling rate during solidification.
Here is a list of defects to keep in mind while designing a part for injection molding. In the next section, we’ll see how you can avoid each of them by following good design practices.
Warping
When certain sections cool faster than others, then the part can permanently bend due to internal stresses.Parts with non-constant wall thickness are most prone to warping.
Sink marks
When the interior of a part solidifies before its surface, a small recess in an otherwise flat surface may appear, called a sink mark.Parts with thick walls or poorly designed ribs are most prone to sinking.
Drag marks
As the plastic shrinks, it applies pressure on the mold. During ejection, the walls of the part will slide and scrape against the mold, which can result to drag marks.Parts with vertical walls are most prone to drag marks.
Knit lines
When 2 flows meet, small hair-like discolorations may develop. These knit lines affect the parts aesthetics, but also they generally decrease the strength of the part.Parts with abrupt geometry changes or holes are more prone to knit lines.
Short shots
Trapped air in the mold can inhibit the flow of the material during injection, resulting in an incomplete part. Good design can improve the flowability of the melted plastic.Parts with very thin walls or poorly designed ribs are more prone to short shots.
What Mistakes Reduces The Lifespan Of Injection Molds
Injection mold damage can be indicated and in some cases increased by mistakes in the parts being made. These mistakes include sink marks, surface delamination, flow lines, burn marks, and flash. In more detail:
1. Sink Marks
Sink marks are a source of further damage that can be inflicted on the mold, further reducing lifespan. These are small depressions localized in the thicker areas of the mold and are caused by incorrect cooling time. The plastic does not cool sufficiently while it is inside the mold, an issue that is usually related to inadequate pressure inside the cavity or too much heat.
2. Surface Delamination
Surface delamination can decrease mold lifespan by increasing wear over the long term. This issue involves thin layers of materials that appear on the part surface and is caused by contamination with unintended materials or release agents. Adjusting the ejection mechanism may remove the need for the use of release agents.
3. Flow Lines
Flow lines indicate either flow rate problems or bad mold design. Flow lines are patterns or lines that appear on parts. Usually caused by varying flow rates which cause the molten plastic to solidify at different rates, this issue is fixed by adjusting injection speed and pressure in order for the cavity to be filled evenly. In more serious cases, this issue can be a sign of bad mold design, in which case the mold must be redesigned.
4. Burn Marks
5. Flash
What Plastics Are Used In Injection Moulding
The names of the plastic injection molding materials sound like chemical words. Polyethylene rhymes with polypropylene, which has a similar acronym to polystyrene, which is challenging enough.
Knowing your application requirements which might change between prototyping and production is important when choosing the proper injection molding material. Any injection molding manufacturer will utilize a variety of plastics to achieve the finest results. Check them out below.
Read Also: How To Test If You Have Mold In Your House
Design Rules For Injection Molding
One of the biggest benefits of injection molding is how easily complex geometries can be formed, allowing a single part to serve multiple functions.
Once the mold is manufactured, these complex parts can be reproduced at a very low cost. But changes to the mold design at later stages of development can be very expensive, so achieving the best results on the first time is essential. Follow the guidelines below to avoid the most common defects in injection molding.
Use a constant wall thickness
Use a uniform wall thickness throughout the part and avoid thick sections. This is essential as non-uniform walls can lead to warping or the part as the melted material cools down.
If sections of different thickness are required, make the transition as smooth as possible using a chamfer or fillet. This way the material will flow more evenly inside the cavity, ensuring that the whole mold will be fully filled.
Make the transition as smooth as possible at section of non-uniform wall thicknessrecommended wall thicknesses
| Material |
|---|
For best results:
What Industries Utilize Plastic Injection Molding
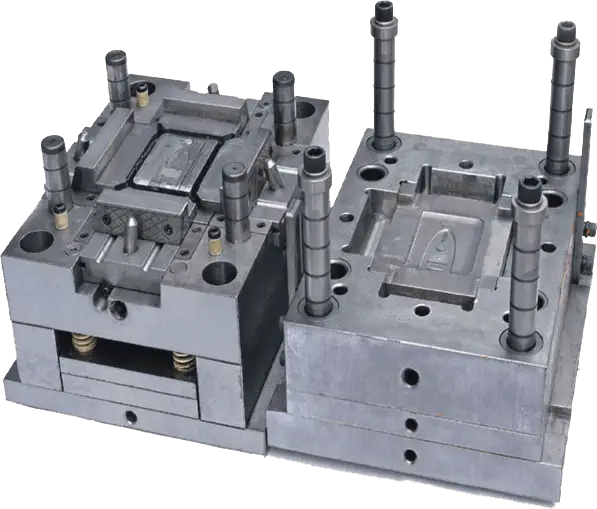
For OEMs in industries of all types, plastic parts are an essential and economical option in product design and production. In most circumstances, it makes sense to find the lowest cost, lowest weight, and most durable material to produce the product needed. Plastic injection molding is an incredibly versatile manufacturing process that plays a critical role in developing products from medical devices to automotive components to appliances and more. In fact, plastics can reduce the weight of parts by 50%, produce less scrap, and be formed into more complex shapes and geometries. Lets review some of the top applications for injection molding and the valuable characteristics of plastic parts for each.
Automotive: Many plastic parts in automobiles require a range of intricate design features to function correctly. Typical injected molded components used in automobiles include bumpers, dashboards, and smaller parts, such as cup holders, mirror housings, and many more. Common characteristics of plastic parts for the automotive industry include:
- Weather and wear-resistant
- High-heat plastic parts maintain integrity in high-temp scenarios
- Effective alternative for discontinued parts
- Lightweight for reduced emissions/energy saving
- Certain polymers stable from the degradation of chemical exposure
- Noise and vibration reduction
- Reduced cost and weight
- Corrosion resistance
- Non-reactive to chemicals
- Reduced cost and weight
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of Mold On Drywall
The Invention Of Injection Molding Up To The Present Day
Hendry then developed the first gas-assisted injection molding system in the 1970s. The technique made it possible to manufacture complex parts, which could be cooled quickly. This greatly improved the flexibility and strength of the manufactured objects while reducing production time and cost. In 1979, plastic production surpassed steel, and in 1990, injection molding made extensive use of aluminum molds. Today, screw injection machines represent the vast majority of injection machines. Other widely used molding methods include blow molding, compression molding, or vacuum molding .
Now, the injection molding market has reached $300 billion. This process produces more than 5 million tons of plastic parts yearly worldwide. Almost all manufacturing sectors use it: electronics, automotive, household goods and appliances, etc. Plastic injection molding remains an affordable and efficient method of producing high-quality parts and products. Recently, the demand for biodegradable materials has increased for environmental reasons.
The technology used today is quite like the one used in the past. However, computers have facilitated the entire design and manufacturing process. Results are also more accurate, and plastic parts are now often the preferred choice for advanced technological and scientific applications.
What Are The Types Of Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is not a one-size-fits-all process. Different techniques can be used to achieve different types of end results.
Standard Molding: This basic technique uses a single color and material to produce the part. It is commonly used to manufacture everything from beverage containers and caps to auto parts and toys.
Overmolding: This is a two-step process used to produce items that require two different types of plastic — for example, a shaped handle with a soft outer material that makes it easier to grip.
First, the substrate part is produced then each part is individually moved to another mold where another thermoplastic is molded over the substrate. The bond between the two materials can be mechanical or chemical.
Insert molding: Insert molding is an application in which a prefabricated part is used as the substrate. This substrate may be made of an alternative material to plastic .
Knobs and dials that have a plastic exterior over a metal interior are examples of insert molding. The substrate is inserted into the mold, then plastic is injected onto it. Typically this process uses thermoplastic resin as the overmolding material.
First, a substrate is injected by the primary press barrel. Then, mold steel is exchanged and a second injection unit molds the second shot. The bond between the materials can be chemical or mechanical.
Read Also: Can Black Mold Cause Neurological Problems
Injection Molding: What It Is How It Works Who Is It For
Ronan Ye
Rapid Prototyping & Rapid Manufacturing Expert
Specialize in CNC machining, 3D printing, urethane casting, rapid tooling, injection molding, metal casting, sheet metal and extrusion
Injection molding is the most popular method for manufacturing plastic parts on the planet, so its not surprising that the global market for the process was valued at almost 260 million U.S. dollars, with projections for continued growth in the foreseeable future.
The technology is used in a wide variety of industries, including aerospace, medical equipment, and automotive, where advanced techniques such as overmolding and insert molding are used to create even the most complex parts with impeccable precision.
And when you consider just the wide range of injection molding benefits, understanding why millions of companies in some of the most demanding industries in the world are using it for bringing their part designs to life.
But why is injection molding machine manufacturing so effective? And how does it work?
To find out, lets dig into the subject and answer all of the important questions, including what it is, the process behind it, its main advantages, and how to choose the right service provider.
Why We Choose Plastic Injection Mold
1) High precision
As a highly accurate processing approach, the plastic injection molding process is able to be used to produce diversified plastic parts of almost any types. Though certain design restrictions do exist, the injection molds are made to ensure the great precision of the molded products. As a matter of fact, the precision of the finished products can be kept within 0.005in.tolerance.
2) High efficiency
Plastic injection molding is known as one of the most commonly used technologies for long production periods because it is very fast. But, how fast? Though its production speed may be dependent on the complexity of the mold structure, there is only about 15 to 30 seconds interval between cycle times.
3) It saves the labor cost
The injection molding equipment requires minimal human supervision, of which the reason is that they usually work with a self-gating and full automatic tool, so as to realize streamlined operation and continuous production.
4) Highly resourceful
Nowadays, a lot of attention is paid to sustainability, so it is very common for product developers to opt for a process that would help with environmental protection and waste elimination. Not only is the plastic injection molding a highly efficient and effective process, it is also very resourceful. The reasons are i. only the needed amount of plastics is used to produce the desired product ii) excessive materials will be recycled for further use.
5) Its flexible
6)Lighter and cheaper
Also Check: How To Detect Mold In House Walls
The Injection Unit Or Plasticizing Unit
How does injection molding work? In the injection unit or plasticizing unit, the plastics are usually fed in granulate form through a hopper and prepared for injection molding. To do this, they must be heated, liquefied, and homogenized.
The machines injection unit, which shapes like a cylinder heats from the outside by heating coils or bands. A screw is rotating inside sizes to fit snugly within the barrel.
While the granules are transported forwards by the screw towards the nozzle, they are also heated, grounded, and mixed or distribute by friction.
The plastic, which is evenly liquefied in this way, is prevented from flowing back when it reaches the nozzle by a non-return valve. This builds up a certain pressure with which the plastic compresses.
How does injection molding work? Then the plastic is pressed through the nozzle with another forward movement. At the same time, the nozzle also takes care of the dosing by closing precisely calculate and thus interrupting the injection.
The auger then retracts to process the next batch of granules. In this injection phase, the material is pressed into the clamping unit under very high pressure of up to 2000 bar, which can be up to 2000 bar. The filling speed must of course be calculated extremely precisely so that no cavities or cracks form in the workpiece.
Produce Plastic Parts With 3d Printed Mold
Making a 3D-printed mold is a straightforward process for people with operational expertise and knowledge of 3D printing. However, for people without expertise, a better option is to outsource molded parts production to a professional. At RapidDirect, we offer 3D printing services to help you create prototypes and production parts.
We are an ISO 9001:2015 certified prototype and part manufacturing company with the right technology, machine, facilities, and teams to handle your project effectively. Moreover, our instant quoting platform gives accurate quotations and DFM analysis on design uploads. Upload your design file today and get a real-time quotation and DFM report within 12 hours.
Recommended Reading: Is Vinegar Or Bleach Better For Killing Mold
Conclusions And Future Trends
Injection molding has become one of the most important methods for processing short and long glass fiber reinforced thermoplastics, and is expected to continue to grow annually for more applications in novel fields such as optics, electricals and electronics, aerospace, biomedicine and communications. New fillers such as benign filler or eco fillers made from recycled paper, structural lignocellulosic fibers from corncobs and high cellulose fiber from wheat straw that are sustainable or recyclable will continue to be developed. Meanwhile, other process variants such as micro-injection molding of micro-and nanocomponents, high speed injection molding of ultra-thin composite parts, new foaming process that produces parts free of sink marks, low in warpage and with a high quality surface, injection molding of long-fiber-reinforced thermoplastics that exhibit good creep resistance and impact performance, and injection molding of conductive thermoplastics that provide effective EMI shielding in engineering applications, etc., will continue to be explored and developed. The injection molding technology will play a very important role in contributing to the growth and success of the plastic composites industry.
Lorraine F. Francis, in, 2016
Electric Injection Molding Machine
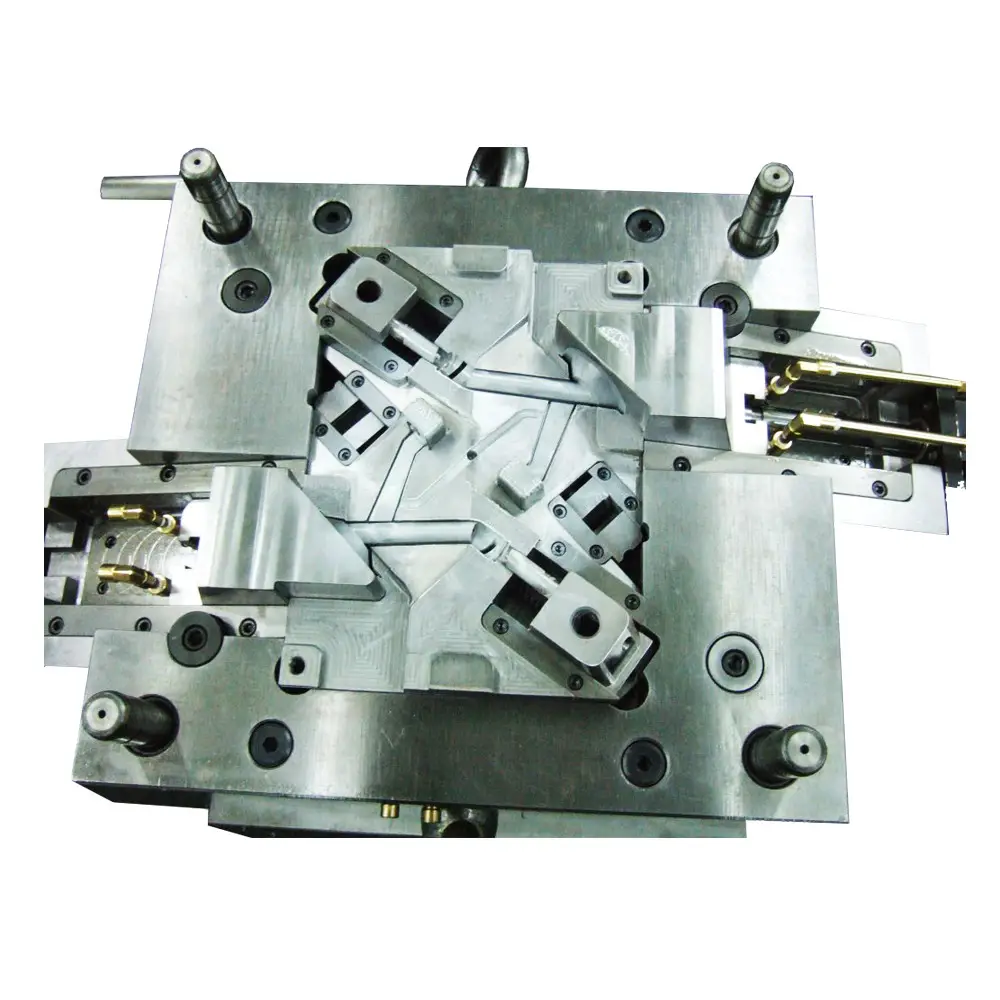
By minimizing energy consumption, the electric press, also known as an Electric Injection Molding Machine, lowers operational expenses. It also addresses some of the hydraulic presss environmental concerns. Manual presses are quieter, faster, and more accurate than electric presses, but they are also more expensive.
Read Also: How To Remove Mold From Headliner
Equipment Used For Injection Molding
Injection molding processes are conducted through special machines that are designed just for that purpose and nothing else. They come in varying sizes and shapes depending on the shape of the product you minted to have at the end of the line, but on a general level, they all work using the same principle. The following are the main machines used in this process.
Is Rotational Molding Right For You
So you need a custom plastic part or product, but you dont know how to get it made.
Is it large or small? Should it be flexible or stiff? Is it round, square, or some weird shape? Do you already have a mold, or do you need to have one made?
This guide will explain the different kinds of molding processes available today to help you discover the ideal process for your product.*Disclaimer: Even though Fibertech exclusively offers rotational molding, weve gone to great lengths to make sure this guide accurately helps you choose the best form of molding for your product. Sometimes, the best choice is rotational molding other times, its another kind of molding. Our goal with this guide is to be as objective as possible while pointing you in the best direction to get your part or product made with the ideal method. If you have questions or comments about this guide, feel free to contact us.
Don’t Miss: Does Bleach Kill Mold On Plastic
How A Plastic Injection Molding Machine Works
To begin the plastic injection molding process, plastic pellets are fed from a hopper into a barrel. The barrel contains an internal auger.
Simply put, an auger is a screw-shaped device that feeds material by rotating. Heater bands on the outside of the barrel heat the barrel and screw, melting the plastic into a molten state.
When the machines cycle is initiated, the mold closes, and the auger plunges forward under high pressure like a giant plunger in a syringe.
In less than a few seconds, the internal auger injects the molten plastic into the empty part of the mold called the cavity. To quickly cool the molten plastic, a coolantusually waterflows in and around the mold through channels, much like an engine block. In typically less than 60 seconds, the plastic solidifies into the shape of the cavity.
After the plastic part solidifies, the mold opens, and the part is ejected. Once the plastic injection molding machine ejects the solidified plastic part, the process can begin again.
Diagram of the plastic injection molding process
Determine The Molding Process
There are different molding processes used in manufacturing plastics. Custom injection molding is one of the most popular techniques used to produce high-volume plastic parts using an open-and-close mold function.
However, the process you choose will depend on different variables. These include your initial design, the quantity of the parts needed, and the overall use of the products. Additionally, working with an injection molder that offers post- molding capabilities can help streamline your process, create efficiencies, and reduce costs. Whether youre looking for post-molding services including hot stamping, inserting, heat staking, or more, some injection molders are equipped to provide turn-key solutions.
Read Also: What Can You Spray On Mold
Uniform Wall Thickness Is Critical
Injection molding necessitates uniform wall thickness. If you were to cut a cross-section of the Panasonic mold above you would notice that the wall thickness is approximately 2-3mm thick throughout. Keeping walls from being too thick is important to prevent inconsistencies in the cooling process resulting in defects like sink marks.
A good rule of thumb is to keep walls less than or equal to 4mm thick. The thicker the walls the more material you will use, the longer the cycle time will be and the higher your cost per part will be.
Conversely, if wall thickness is any thinner than 1mm or so you might experience trouble filling the mold tool . Designers can compensate for this potentiality by using a material with a higher melt flow index like Nylon which is often suitable for walls as thin as 0.5mm.
Different manufacturing techniques like CNC dont require uniform wall thickness at all.